Digital Human Resource Management is not a bot. The Digital HRM (Human Resource Management) is a human being that knows how to use available technology & understands that the nature of work and employment has changed.
In the text that follows, we shall discuss our experiences working in Human Resources Management, either as Manager, MD or as Team Leader of a consulting Team that modernizes & develops Human Resources Management.
We intend to show a new path for HRM, not just to follow the trend.
The first observation that we have confirmed with ours & our team’s long experience, is that HR management is both improving, as well as, significantly contributing to the Growth of a Company.
 Following Pareto’s law, still nowadays, 80% of the classical HRM’s (Human Resource Management’s) time is devoted to trivialities and only 20% to vital, strategic duties.
Following Pareto’s law, still nowadays, 80% of the classical HRM’s (Human Resource Management’s) time is devoted to trivialities and only 20% to vital, strategic duties.
The modern HRM (Human Resource Management) can be freed to a great extent from the drudgery of HR duties. Thanks to the new digital tools, those jobs which have more to do with accounting or compliance, can be largely alleviated.
Even for recruitment purposes, software can release HRM from 90% of the job of  recruitment, by objective screening of data from a candidate’s CV, evaluating qualifications, career history, social media profile and other openly available data, reducing interview time to the 3-5 final selection choices.
recruitment, by objective screening of data from a candidate’s CV, evaluating qualifications, career history, social media profile and other openly available data, reducing interview time to the 3-5 final selection choices.
The two principal strategic duties of HRM (Human Resource Management) were and always are:
- To enrich the Company with new talent.
- To preserve and develop the Company’s existing talent.

To achieve those, HRM (Human Resource Management) does not need to be a master of digitalization but rather understand what digitalization means for the human talent needed by a Company and for the new nature of employment itself. In other words, to have a deep understanding of the new Business Model that a Company should operate in and as a consequence, the talent required to support it.
The nearest parallel of what is happening today is the introduction of steam engines in sailing ships. For thousands of years ships were using sails as means of propulsion. Within two generations this was replaced completely by engines. Sailing a ship survived only as a word and a new class of professionals took over from the sailing men, engineers. The basic maritime virtues required from the Captain and the deck officers were not abolished but were dramatically modified while new skills came to the fore managing a ship.
The imaginary HRM (Human Resource Management), working for a shipping line, did not need to be an engineer. To succeed in the job, understanding of a ship’s engineering requirements, was a prerequisite.
So is with the modern HRM (Human Resource Management). It must understand that a Company needs completely new skills & competencies to survive and succeed. Moreover, it is the job of the HRM to find and develop the new talent. Rapid advances in digitalization change the Business Models that the Companies operate with, as technological changes are exponentially overtaking levels of productivity.
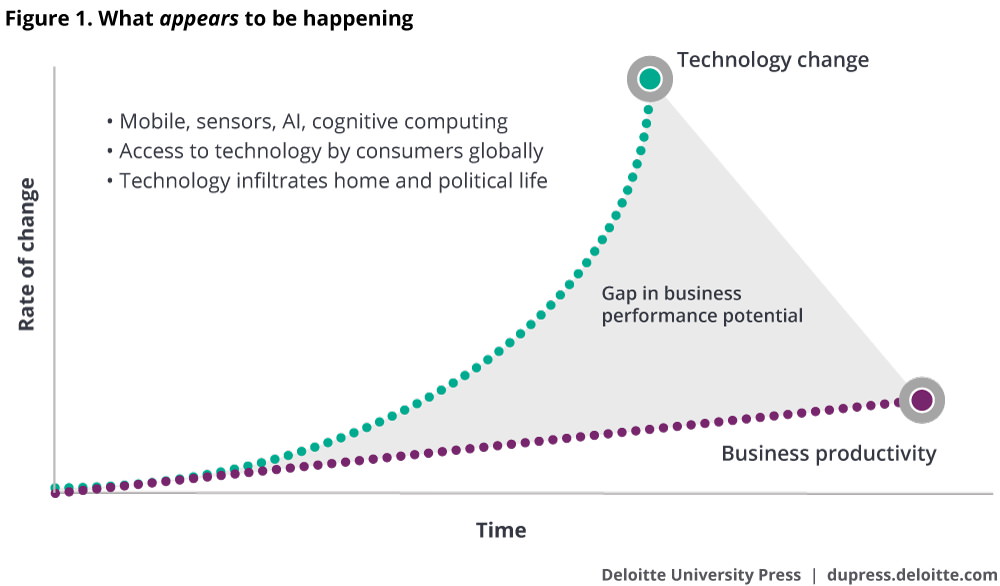
The above graph, maybe the most succinct & impressive of its kind, highlights in a dramatic way the great gap between the capabilities of technology and its exploitation. The principal reason is of course that humans do not yet fully understand how to fully exploit the new technologies.
The major part of the new digital HRM’s (Human Resource Management’s) job is to help fill this gap.
While many people continue to seek employment for physiological reasons of subsistence, talented people, usually of the younger generation, are not only looking for that. They also look to have some fun doing their job, particularly some freedom to create, within an organization.
We must make clear that employee satisfaction should not be a Company’s aim per se. It is however necessary, as satisfied employees do the job better and make the contributions that an employer needs. If they don’t, all that the employer does to provide an environment that satisfies employees is for naught.
 Finding and keeping the new talented and productive employees, endowed with the knowledge and ability to operate and create in a continuously more digitalized and automated environment, is the HRM’s most strategic and demanding challenge.
Finding and keeping the new talented and productive employees, endowed with the knowledge and ability to operate and create in a continuously more digitalized and automated environment, is the HRM’s most strategic and demanding challenge.
Digital competence, according to Diego Martinez, is the attitude and ability that enables employees to embrace technology, collaborate with others and work effectively in a modern, digital environment.
The new talented employees that have the digital competence required to cover the needs of the 4th Industrial Revolution, are millennials in continuously increasing numbers, to whom higher responsibilities must be entrusted vs the same age in a previous generation.
Millennials are an “entitlement” generation. They demand job satisfaction and more. They are three times as likely to change jobs than their previous generation counterparts, according to a relevant Gallup’s report. What keeps them in a Company is job engagement. They expect their career development to be visible, as well as, to be able to create so as to reach their “full potential”.
To consider them “spoiled” does not help. They lack experience and perhaps “maturity” hence they need our guidance and support.
The fact remains that they are needed.
The principal duty of the HRM (Human Resource Management) in our times is to help  increase the Digital competence of a Company. The enriched EU definition is: “Digital competence involves the confident and critical use of information Society technology (IST) for work, learning and communication. It is underpinned by basic skills in ICT: the use of computers to retrieve, access, store, produce, present and exchange information, and to communicate and participate in collaborative networks via the Internet. It must be added that use of big data handling, analytics, IoT, AR, AI, Robotic process and the rest of the available tools must be used as required”.
increase the Digital competence of a Company. The enriched EU definition is: “Digital competence involves the confident and critical use of information Society technology (IST) for work, learning and communication. It is underpinned by basic skills in ICT: the use of computers to retrieve, access, store, produce, present and exchange information, and to communicate and participate in collaborative networks via the Internet. It must be added that use of big data handling, analytics, IoT, AR, AI, Robotic process and the rest of the available tools must be used as required”.
It is one of the EU’s key competencies for lifelong learning. And it is not something that uniquely applies to young people. It affects all of us and how we learn, survive and grow professionally.
What is the most difficult and rewarding duty for the Human Resource Management is to find the suitable Knowledge Workers.
![]() Oracle has grouped them into four areas:
Oracle has grouped them into four areas:

Explorer, Thinker, Socializer & Achiever.
While this is valid, no HRM (Human Resource Management) is ever going to be fully successful until he/she allies with the CIO, CDO, or whatever the role is called in a specific Company. Whatever are the job definition variances, it is essentially the C-suite Officer who has the Leadership ability and the technical competency and know-how to change the culture and transform a Company successfully and continuously to a digitally agile one.
It is possible that the HRM (Human Resource Management) will search to find such one. The position is new, Company needs vary and so do the candidates. They usually are younger than their other C-suite colleagues. Achieving digital competence must be a top priority for every organization.
The HRM’s (Human Resource Management’s) role is not diminished but rather enhanced in the digital era. The recently called Human Capital Officer, is one of the most valuable and needed strategic partner linking the new technologies with the employees that use it.
 John Naisbitt said: “The big challenge of the 21st century is not the technology. It is the attitude towards the human being”. The human capital management, both to talents and to lower employees is more crucial than ever. Companies have to place machines, systems, robots but have to choose and retain humans, who will in turn create the “next day”, ensuring a company’s sustainability and growth.
John Naisbitt said: “The big challenge of the 21st century is not the technology. It is the attitude towards the human being”. The human capital management, both to talents and to lower employees is more crucial than ever. Companies have to place machines, systems, robots but have to choose and retain humans, who will in turn create the “next day”, ensuring a company’s sustainability and growth.

