Algae project is “magic” photosynthetic organism. The latest year is being used as the core of various types of circular economy models. Economies that are relating to wastewater treatment and carbon emissions.
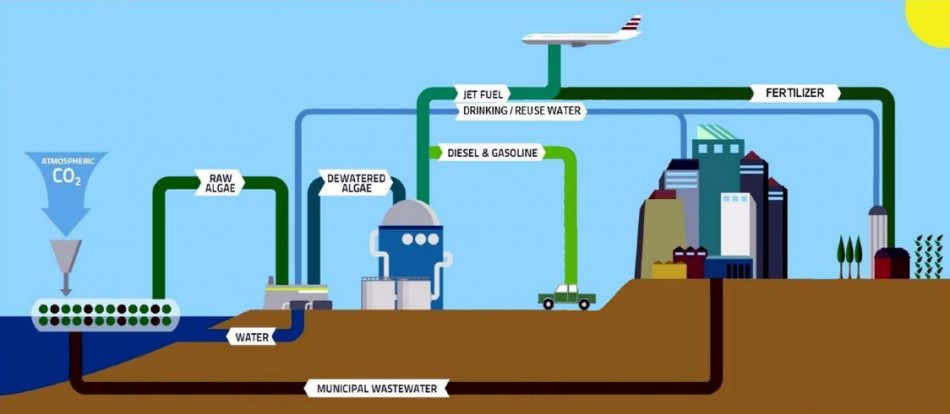
In the model suggested from http://algaesystems.com/ wastewater go to strong plastic bugs in an offshore plantation for the cultivation of algae. Then sunlight and CO2, green algae and associated microbes rapidly convert nutrients and organic carbon from wastewater into renewable biomass. Out of cultivated algae that grow rapidly (sucking CO2 from the atmosphere on the same time) you can produce biofuel, fertilizers and bioenergy.
Many species of microalgae have high lipid contents that can readily extracted and converted to biodiesel. Similarly, their high content of fermentable sugars makes them suitable for bio-ethanol production.
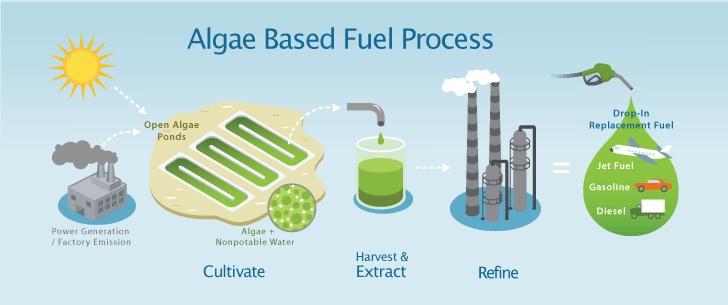
Microalgae can therefore generate a whole suite of bioenergy products:
- Bio-diesel
- Bio-plastic
- Bio-butanol
- Bio-gasoline
- Methane
- Ethanol Straight Vegetable Oil (SVO)
- Aviation fuel
- Hydrocracking to traditional transport fuels
Over the years several solutions has been presented with algae for example:
1. Algae Biofuels for Airlines that will replace kerosene
 http://www.reuters.com/article/us-airbus-germany-biofuels-idUSKCN0Z117F
http://www.reuters.com/article/us-airbus-germany-biofuels-idUSKCN0Z117F
https://www.treehugger.com/aviation/worlds-first-flight-powered-by-100-algae-biofuels-completed.html
http://inhabitat.com/eads-develops-first-algae-fuel-powered-aircraft/
2. In the project AlgaTec2 a system efficient to treat olive washing water (WW) was introduced that could remove the pollution load, producing water of drinking quality that could be reused in the process (See http://algatec2.eu/ )

3. The ability of algae to sucking CO2 was utilized in cement production. Cement production is a dirty process. However, there are two examples in Sweden and in Canada where they make a carbon free cement, driving the CO2 into algae cultivation in closed-loop process. Producing either biofuel or additives for chicken and fish food.
- https://qz.com/1010273/the-algoland-carbon-capture-project-in-sweden-uses-algae-to-help-the-country-reach-zero-emissions/
- http://inhabitat.com/company-uses-cement-plants-co2-emissions-to-create-algae-based-biofuel/
4. Another tremendous ability of algae is that it can replace petroleum plastics with biodegradable bio-plastics. Solaplast, harnesses the potential of algae to make bio-plastics for the replacement of traditional petroleum-based plastics and for the reduction of biodegradable plastic costs. http://algix.com/from-plastic-pollution-to-an-algae-solution/
5. Microalgae are not only being used in the plastic industry but they are also being used in the cosmetics Various Companies are coming up with products that use Microalgae to treat various skin conditions and problems. Different types of skin whitening creams and anti-aging creams can be made using Microalgae as their base ingredient. Currently, Microalgae are being used in moisturizing creams but they can also be used for treating other skin problems such as pigmentation.

6. Algae in Nutrional sector: another area in which Microalgae is being used is in the global food market (drinks, yogurts, supplements, etc.). Microalgae based foods and supplements are gaining popularity. Microalgae like chlorella and spirulina are already being used as dietary supplements in their pure forms. That is why Japan is now the biggest consumer of these products. Studies have shown that Microalgae spirulina has over 30 healthy nutrients that are beneficial for the body. 100 grams of spirulina can yield about 50-80 grams of vegetable proteins. Apart from these proteins, spirulina also provides beneficial vitamins and minerals such as calcium, magnesium and beta carotenes.

7. Algae’s natural bioluminescence Designer Gyula Bodonyi has created the Algaebulb; a light bulb in which the algae within fuels an LED via the oxygen it emits as it grows. Since algae thrive on carbon dioxide, the bulb also helps to lessen greenhouse gases,  and cleans the air in its immediate vicinity by sucking it in through an air outlet in the polycarbonate shell. Although the teardrop-shaped bulb is quite small, its potential impact is enormous: an extraordinary amount of energy could be saved if everyone in North America installed just a few of these in their homes. http://inhabitat.com/gyula-bodonyis-algae-powered-led-is-truly-a-green-light-bulb/
and cleans the air in its immediate vicinity by sucking it in through an air outlet in the polycarbonate shell. Although the teardrop-shaped bulb is quite small, its potential impact is enormous: an extraordinary amount of energy could be saved if everyone in North America installed just a few of these in their homes. http://inhabitat.com/gyula-bodonyis-algae-powered-led-is-truly-a-green-light-bulb/
8. A team of researchers and designers from Cambridge University are working on the development of bio-photovolaic (BPV) devices fueled by moss and algae. When those  tiny, fast-growing plants photosynthesize, they create a startling amount of energy; that energy can be extracted to power photovoltaic panels, which in turn can be used to power anything. Since algae regenerates so very quickly, this kind of technology could be a brilliant alternative to silicon-based solar panels, which are both resource-heavy to develop, and expensive to create. http://inhabitat.com/moss-table-by-biophotovoltaics-generates-electricity-through-photosynthesis/
tiny, fast-growing plants photosynthesize, they create a startling amount of energy; that energy can be extracted to power photovoltaic panels, which in turn can be used to power anything. Since algae regenerates so very quickly, this kind of technology could be a brilliant alternative to silicon-based solar panels, which are both resource-heavy to develop, and expensive to create. http://inhabitat.com/moss-table-by-biophotovoltaics-generates-electricity-through-photosynthesis/
9. In Hamburg, Germany, an Algae-powered building was designed by Splitterwerk Architects. Its entire facade is covered in shutters filled with bio-reactive micro-algae, which create heat that’s harvested and used to power the structure. It’s a great source of clean, renewable energy, and the louvers that house the living algae not only encourage the plants within to flourish—they also provide shade for the building’s interior… which in turn reduces the need for air conditioning or ceiling fans

It can be concluded that in the future algae can be the vital part of a circular economy based model, that will utilize wastewater and the carbon emissions of the cities and its industries for the production of a series of products in a greener, faster, cheaper manner.
Reports
- THE MICROALGAE/BIOMASS INDUSTRY IN JAPAN http://cdnsite.eu-japan.eu/sites/default/files/publications/docs/microalgaebiomassiindustryinjapan-herrador-min16-1.pdf
- http://www.ieabioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/IEA-Bioenergy-Algae-report-update-20170114.pdf

